How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, essential flight techniques, and best practices for capturing stunning visuals.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Understanding the fundamental components of your drone, such as the flight controller, propellers, and motors, is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Proper pre-flight checks are equally vital, ensuring your drone is calibrated and your battery is fully charged. Mastering basic flight controls—altitude, direction, and speed—will lay the foundation for more advanced maneuvers. Throughout this guide, we emphasize safety and adherence to local regulations, ensuring your drone flying experience is both enjoyable and legal.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts and their functions, enabling you to troubleshoot issues and appreciate the intricate mechanics involved in flight.
Main Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone comprises several key components working in concert. These include the frame, which provides structural support; motors, responsible for propulsion; propellers, generating thrust; a flight controller, the drone’s “brain”; an electronic speed controller (ESC), managing motor speed; a battery, providing power; a GPS module, aiding navigation and positioning; and a camera, for capturing images and videos. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s overall performance.
The Flight Controller’s Role in Drone Operation, How to operate a drone
The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone. It receives input from various sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers) and uses this data to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote controller. It constantly adjusts motor speeds to compensate for external factors like wind and maintain the desired flight path. Essentially, it’s the drone’s autopilot.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will ensure you’re well-prepared for a safe and productive flight experience with your drone.
Drone Propeller Types and Their Impact on Flight
Different drone propellers offer varying levels of thrust, efficiency, and noise. Common types include standard propellers, which offer a balance of performance and noise; low-noise propellers, designed for quieter operation; and high-performance propellers, optimized for speed and maneuverability. The propeller’s pitch, diameter, and material all affect the drone’s flight characteristics.
Comparison of Drone Motors
| Motor Model | KV Rating | Max Current (A) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor A | 2300 | 30 | 35 |
| Motor B | 2800 | 40 | 42 |
| Motor C | 1800 | 25 | 30 |
| Motor D | 2500 | 35 | 38 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight checks are essential for safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or equipment damage. This section Artikels a comprehensive checklist and procedures to ensure your drone is ready for flight.
Step-by-Step Pre-Flight Drone Inspection
- Visually inspect the drone for any damage to the frame, propellers, or other components.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Power on the drone and remote controller, ensuring a stable connection.
- Perform a pre-flight check within the drone’s app or software, if applicable.
- Check for any obstructions in the intended flight area.
Importance of Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and sensors is crucial for accurate flight and stability. An improperly calibrated compass can lead to inaccurate heading information, while faulty sensors can affect the drone’s ability to maintain its position and orientation. Calibration procedures typically involve specific movements or maneuvers as Artikeld in the drone’s manual.
Battery Level Checks and Charging Procedures
Always check the battery level before each flight. Use only the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Overcharging or using incompatible chargers can damage the battery and pose a safety risk.
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A visual representation (flowchart) would be beneficial here, illustrating the logical sequence of pre-flight checks. However, creating a flowchart in plain text HTML is not easily achieved and would be difficult to render clearly. The steps Artikeld above provide the sequential order for pre-flight procedures.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are paramount for preventing accidents and damage. This section details the steps for safe launches and landings, covering various terrains and emergency procedures.
Safe Drone Launch Procedures
Begin by selecting a suitable, open area free from obstacles. Power on the drone and remote, ensuring a strong connection. Carefully lift the drone, allowing the propellers to spin up. Gently increase the throttle to initiate a controlled ascent, maintaining visual contact at all times.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques for Different Terrains
The ideal takeoff and landing techniques vary depending on the terrain. For flat, open areas, a vertical ascent and descent is usually sufficient. However, uneven terrain or slopes may require more careful maneuvering to avoid collisions. Wind conditions also significantly impact takeoff and landing.
Obstacle Avoidance During Takeoff and Landing
Always maintain awareness of your surroundings. Avoid launching or landing near trees, buildings, or other obstacles. Use the drone’s sensors and camera to assess the environment and plan your flight path accordingly. Practice makes perfect in judging distances and clearances.
Emergency Procedures During Takeoff or Landing
In case of unexpected events, such as a loss of control or a low-battery warning, prioritize a safe landing. Immediately reduce throttle to slow the drone’s descent. If possible, attempt a controlled landing in a safe, open area. Familiarize yourself with your drone’s emergency stop procedure, if available.
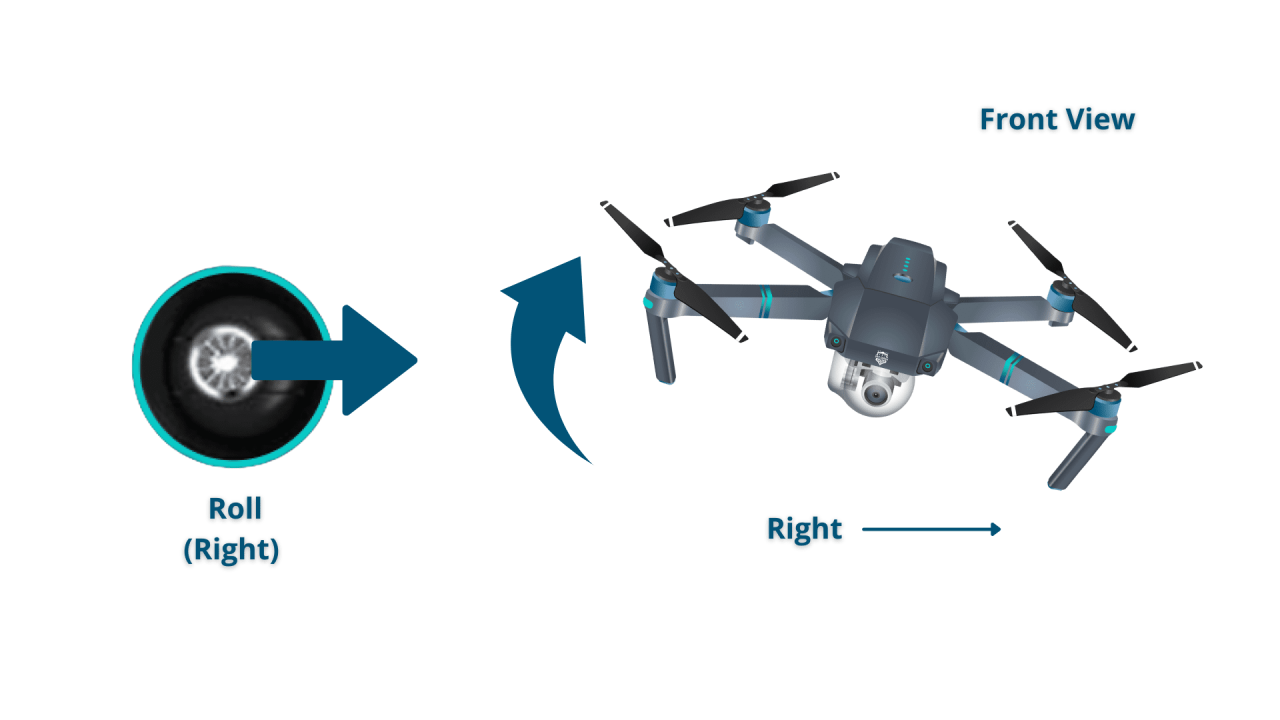
Basic Flight Controls
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section describes the functions of a typical drone remote and how to perform basic maneuvers.
Functions of Drone Remote Control Sticks and Buttons
Most drone remotes feature two joysticks (sticks) controlling pitch/roll and yaw/throttle. Buttons typically control camera functions, return-to-home (RTH), and other features. The specific functions may vary depending on the drone model and manufacturer.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
The throttle stick controls altitude, while the other stick controls the drone’s direction and speed. Moving the sticks in different directions allows for precise control over the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space. Practice is key to developing smooth and controlled movements.
Drone Stability and Its Maintenance
Drone stability is maintained through a combination of the flight controller’s algorithms, sensor data, and motor control. Factors like wind and battery level can affect stability. Proper calibration of the sensors and careful piloting are crucial for maintaining stability.
Performing Basic Flight Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a stationary position), turning (rotating the drone around its vertical axis), and moving forward, backward, and sideways. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more advanced techniques.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight controls, you can explore more advanced maneuvers and techniques. This section covers flying in challenging conditions and navigating complex environments.
Performing Advanced Maneuvers (Flips and Rolls)
Some drones allow for advanced maneuvers such as flips and rolls. These require precise control and should only be attempted in a safe, open area after mastering basic flight. Always consult your drone’s manual for instructions on performing these maneuvers safely.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires more skill and attention. Adjust your flight style to compensate for wind gusts, using smoother and more deliberate movements. Avoid flying in extremely windy conditions, as it can lead to loss of control.
Navigating Complex Environments and Obstacles
Navigating complex environments requires careful planning and precise control. Use the drone’s camera and sensors to assess the environment and plan your flight path accordingly. Practice flying around obstacles in a controlled setting before attempting more challenging environments.
Tips for Improving Drone Piloting Skills
- Practice regularly in a safe environment.
- Start with basic maneuvers and gradually progress to more advanced techniques.
- Watch tutorial videos and read online resources.
- Join a drone community or club to learn from experienced pilots.
- Understand your drone’s limitations and capabilities.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. This section covers camera settings, shot composition, and techniques for capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Drone Camera Settings and Their Impact on Image Quality
Drone camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance significantly impact image quality. Understanding these settings allows you to tailor your images to specific lighting conditions and desired effects. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your style.
Composing Shots for Optimal Visual Impact
Effective shot composition is crucial for creating visually appealing aerial footage. Consider elements such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry to enhance the impact of your images. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique and compelling shots.
Capturing Smooth and Stable Aerial Footage

Smooth and stable footage is essential for professional-looking videos. Use techniques such as slow and deliberate movements, and consider using a gimbal for added stability. Post-processing can also help to smooth out minor shakiness.
Comparison of Drone Camera Features
| Camera Model | Sensor Size | Resolution | Video Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera X | 1/2.3″ | 4K | 60fps |
| Camera Y | 1″ | 4K | 120fps |
| Camera Z | 1/1.7″ | 1080p | 30fps |
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and legal drone operation requires adherence to local regulations and safety precautions. This section details important safety considerations and legal requirements.
Adhering to Local Drone Regulations and Laws
Always check and comply with local drone regulations and laws before flying. These regulations often specify airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Ignoring these rules can result in fines or legal consequences.
Airspace Restrictions and Identification
Airspace restrictions are designated areas where drone operation is limited or prohibited. These restrictions may be due to airport proximity, national security concerns, or other factors. Use online resources or apps to identify airspace restrictions before flying.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is learning about pre-flight checks and procedures, which are essential for safe and responsible operation. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including flight planning and emergency procedures, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these fundamentals will allow you to confidently and safely navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
Safety Precautions While Operating a Drone
Always maintain visual contact with your drone during flight. Avoid flying near people or property. Be mindful of wind conditions and weather forecasts. Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Regularly inspect your drone for any damage or wear and tear.
Scenarios Where Drone Operation Might Be Restricted
Drone operation may be restricted near airports, military bases, prisons, and other sensitive areas. Flying in crowded areas or during inclement weather is also discouraged. Always prioritize safety and respect local regulations.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps to resolve connectivity problems, low battery warnings, and other issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Their Causes
Common issues include connectivity problems (loss of signal), low battery warnings, motor failures, and GPS signal loss. These issues can often be traced to low battery, interference, faulty components, or software glitches. Proper maintenance and regular inspections can help prevent many of these issues.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
Connectivity problems can be caused by interference, distance from the controller, or faulty equipment. Try moving to an area with less interference, ensuring the drone and controller are within range, and checking for any physical damage to the antennas.
Handling Low Battery Warnings and Potential Failures
Low battery warnings should be taken seriously. Immediately initiate a safe return-to-home (RTH) procedure if possible. Never let the battery completely drain, as this can damage the battery and potentially cause a crash.
Basic Drone Maintenance Guide
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This includes cleaning the propellers and frame, checking for loose screws or connections, and inspecting the battery for any signs of damage. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations is crucial.
Drone Battery Management
Proper battery care is crucial for extending the lifespan and ensuring the safe operation of your drone. This section covers battery types, safe charging procedures, and signs of battery degradation.
Importance of Proper Battery Care and Storage
Proper battery care includes avoiding extreme temperatures, fully charging and discharging the battery periodically, and storing the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. This helps to maintain battery performance and extend its lifespan.
Different Battery Types Commonly Used in Drones
Common battery types include Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries, known for their high energy density and lightweight nature. Understanding the specific type of battery in your drone is crucial for proper charging and handling.
Safe Charging Procedures for Drone Batteries
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Never leave LiPo batteries unattended while charging and ensure adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Overcharging or improper charging can be dangerous.
Signs of Battery Degradation and the Need for Replacement
Signs of battery degradation include reduced flight time, increased charging time, and swelling or bulging of the battery. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to replace the battery to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Drone Software and Apps: How To Operate A Drone
Drone software and apps provide essential functionality for controlling, monitoring, and managing your drone. This section explores common features and functionalities.
Functionality of Common Drone Apps and Software

Drone apps and software typically provide features for controlling the drone’s flight, adjusting camera settings, viewing live video feeds, accessing flight logs, and updating firmware. The specific features may vary depending on the drone model and app.
Updating Drone Firmware
Regularly updating your drone’s firmware is essential for maintaining optimal performance and accessing new features. Firmware updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new functionalities. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for updating firmware.
Accessing and Interpreting Drone Flight Logs
Drone flight logs record data about your drone’s flight, including GPS coordinates, altitude, speed, and battery levels. This data can be useful for analyzing your flights, identifying potential issues, and improving your piloting skills.
Features Commonly Found in Drone Control Apps
- Live video feed
- Flight controls
- Camera settings adjustments
- Return-to-home (RTH) function
- Flight data logging
- Firmware updates
- Battery monitoring
- GPS map integration
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical understanding and responsible piloting. By mastering the pre-flight procedures, basic and advanced flight controls, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember that consistent practice and a commitment to safe operation are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. With this knowledge, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial flight, capturing stunning imagery and pushing the boundaries of your creative vision.
Q&A
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and flight stability.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it doesn’t work, attempt to regain connection manually. If unsuccessful, report the incident to relevant authorities.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What are the legal requirements for flying a drone in my area?
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority or relevant government agency to understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying.
